Facial pain pathologies
Finding the right diagnosis in a patient with facial pain is a big challenge. The following flowchart described by J.M.Zakrzewska n British Journal of Anaesthesia ( BJA: British Journal of Anaesthesia, Volume 111, Issue 1, July 2013, Pages 95–104,)
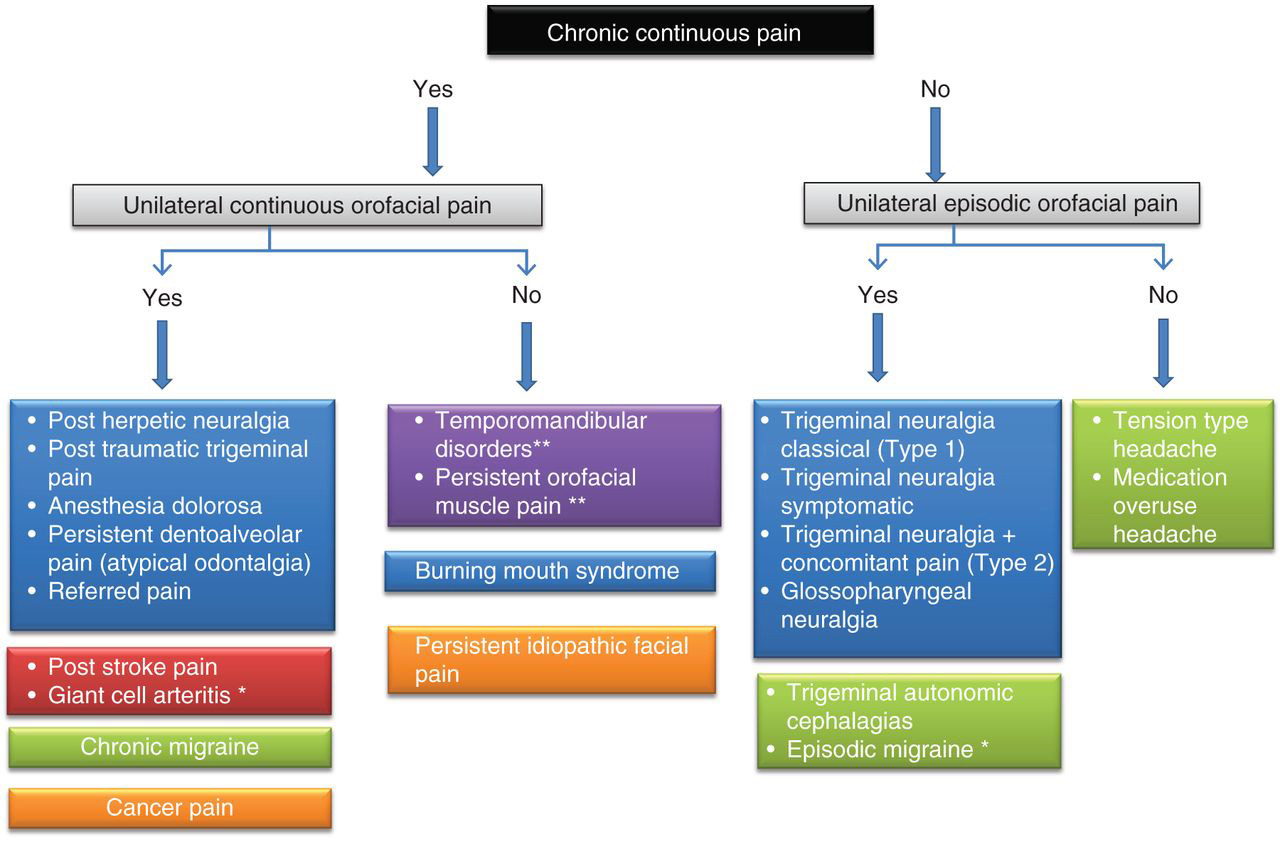
We shall discuss about the following two entities which are relevant in neurosurgery.
Trigeminal neuralgia
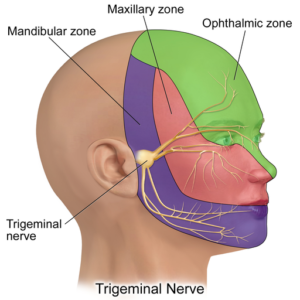
It is a condition that causes sudden, brief episodes of severe stabbing or electric shock-like pain in parts of the face usually on one side. Pain may be triggered by touch or sounds, or by everyday activities such as brushing teeth, chewing, drinking, eating, shaving and light touch on the face. Trigeminal neuralgia is usually caused by the compression of the trigeminal nerve by an artery or a vein, but it can also occur with no apparent cause.
MRI of the brain in most of the cases show a vascular conflict or atleast the vessel being in very close proximity to the cisternal portion of the trigeminal nerve.
Treatment: Medication is always the first line of treatment for patients with trigeminal neuralgia. Commonly used medications are as follows:
- Carbamazepine
- Oxcarbamazepine
- Gabapentin
- Baclofen
These medicines are used in a step ladder fashion. Patients who continue to experience the pain despite the best medical management will require surgery.
Microvascular decompression is the surgical procedure for treating trigeminal neuralgia. In the surgery, a small incision is made behind the ear and a small hole in the skull is made. The trigeminal nerve is exposed, and the blood vessel (artery or vein) compressing the trigeminal nerve is identified. This blood vessel is moved away from the nerve and a padding made of Teflon felt is placed between them.
Other procedures advocated for trigeminal neuralgia include, peripheral nerve blocks, gasserian ganglion block, radiofrequency ablation, GKRS and others.
Glossopharyngeal neuralgia
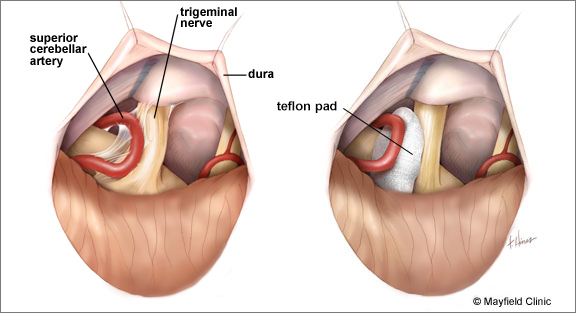
The superior cerebellar artery is adherent to the trigeminal nerve causing compression and painful trigeminal neuralgia attacks.
Glossopharyngeal neuralgia is a condition that causes sharp, stabbing, or shooting pain in the throat area near the tonsils, the back of the tongue or the middle ear. Glossopharyngeal neuralgia is usually caused by the compression of the glossopharyngeal nerve by an artery or a vein, but it can also occur with no apparent cause.
Medical neuralgia is similar to trigeminal neuralgia. If medicines fail o give relief then the patient requires surgery – Microvascular decompression. The surgery is similar to the one for trigeminal neuralgia, except that the compression on glossopharyngeal nerve is relieved by interposing a Teflon felt. Sometimes if a tumour or elongated styloid process is the cause for the pain then a different surgery may be required.
GENERAL ENQURIES
186 0208 0208
+91 8884415615 | +91 8884458890
- gouthamcugati@gmail.com
- Narayana Multispecialty Hospital.
CAH/1, 3rd Phase, Devanur, Ring Road,
Mysore – 570019
OFFICE HOURS
| Monday – Saturday | 09:00 AM – 5:00 PM |
